What types of tax benefits are available for IT and GameDev companies?
Tax incentives continue to be a key tool used by governments worldwide to attract digital and R&D companies. This is especially true for corporate income tax (CIT), which is often considered one of the most burdensome taxes. Experts from Futura Digital shared insights in a column for App2Top about the most relevant types of CIT incentives for IT and GameDev companies that are in demand among their clients.


Alexandra Kurdyumova, co-founder of Futura Digital, and Roman Motorin, a lawyer at Futura Digital
1. Deductions for R&D and Software Development
What is the incentive? The ability to write off software development expenses at a rate exceeding 100% instead of capitalizing them.
Where applied (examples) — Czech Republic, Denmark.
Relevant for companies with high development costs, startups with high levels of expenditure.
Details
Typically, a company that incurs such expenses can proceed in one of the following ways:
- write off these expenses immediately (if permitted by the specific country's tax legislation);
- capitalize them as the cost of intangible assets.
Some jurisdictions allow these expenses to be written off immediately, and even at a rate higher than 100%. This means the company can increase its development expenses in its reports, thereby reducing the profit tax amount.
Example
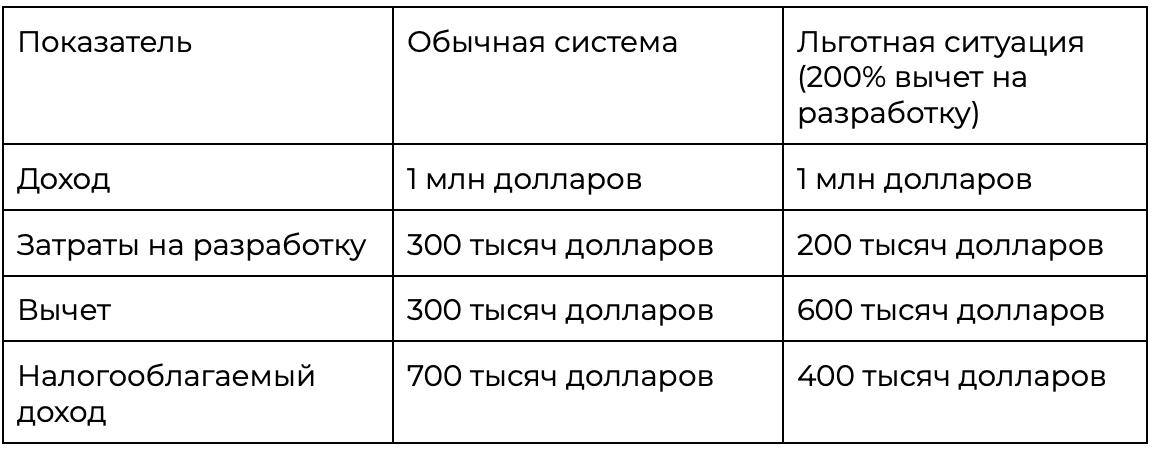
Consider a company with a revenue of $1 million in 2024 (income excluding expenses) and spending $300,000 on development during 2024. For simplicity, let's assume the company has no other expenses.
Thanks to a 200% deduction from actual costs, the company reduces its taxable profit from $700,000 to $400,000, resulting in a lower tax payment.
Effect of the incentive
The more a company spends on development, the less it pays in profit tax, meaning a larger portion of its profit goes untaxed.
Important! If your company is not yet profitable but already incurs significant development costs, consider the rules for carrying forward these deductions. In the Czech Republic, taxpayers can carry forward development deductions up to three years, allowing you to plan the product release date to utilize accumulated deductions.
2. Tax Deferral
What is the incentive? You do not pay corporate income tax until you decide to distribute dividends.
Where applied (examples) — Estonia, Georgia.
Relevant for holding companies, venture funds investing in IT and GameDev, cost centers, particularly those not related to software development (e.g., advertising and traffic acquisition costs).
Details
Corporate income tax is usually paid annually. For example, within a few months after the end of 2024, a company would pay tax on the profits earned in 2024. After the end of 2025, on profits earned in 2025, and so on.
Example
If a company earns a profit of $500,000 for the year 2024, in Estonia or Georgia, the company is not required to pay corporate income tax until dividends are distributed.
This tax incentive has a temporary effect. The company is not taxed on its profits until dividends are distributed, allowing it to reinvest in business and assets without paying corporate income tax. This approach encourages companies to acquire new assets.
For instance, it allows the creation of a holding company in Estonia or Georgia to purchase new assets: shares of other companies, stock options, other financial instruments, new intellectual property (IP) assets, and other investments to scale your business.
3. Tax Reduction through the IP-Box Regime
What is the incentive? Corporate income tax is reduced by applying a lower rate or reducing the tax base.
Where applied (examples) — Cyprus, UAE, Kazakhstan.
Relevant for companies engaged in both development and publishing/licensing of games/software.
Details
This mechanism allows the reduction of corporate income tax for companies developing software in the jurisdiction. Each jurisdiction offers specific ways to reduce the tax:
- in Kazakhstan, the tax base is reduced by 100%;
- in Cyprus, the tax base is reduced by 80%;
- in the UAE, the corporate income tax rate is 0%.
These tax incentives are only applicable to the part of the profit derived from the use of intellectual property. This part is determined by the nexus ratio—the ratio of qualified development expenses to total development expenses.
Nexus ratio formula
NR = (CQ * 130%) / CT, where
- NR – nexus ratio;
- CQ – qualified development expenses (e.g., developer salaries; expenses for outsourcing development to independent contractors, etc.);
- CT – total development expenses incurred by the company (qualified development expenses + all other development expenses).
In other words, software development performed by employed staff or independent contractors increases the nexus ratio. Purchasing rights to ready-made software or transferring development to affiliates lowers the ratio. In any case, it cannot exceed one.
After calculating this ratio, the profit generated from the IP is multiplied by the nexus ratio. The result is the share of profit eligible for the tax incentive.
Example
If the nexus ratio for a company in the UAE is 80%, and the company earns a profit of $1 million (inclusive of expenses), then the 0% tax rate is applied to 80% of this amount, i.e., $800,000. The remaining $200,000 will be taxed at a rate of 9%.
To simplify the tax calculation process, we have developed a simple tool using spreadsheets to help understand the IP-box regime principle. It can be found here.
The effect of this tax incentive is a reduction in the actual corporate income tax paid. However, it also has its drawbacks:
- requires more complex and bureaucratic accounting;
- available only to companies incurring development costs (employee salaries, independent developers);
- the company must derive income solely from IP (e.g., royalties).
***
We have examined three of the most popular types of tax incentives for IT and GameDev companies, but there are significantly more.
It is important to note: each jurisdiction has its own specifics, and choosing the optimal strategy depends on the particularities of your business. Consulting with experts will help you develop a personalized plan that maximizes the benefits of tax incentives for your company.